Introduction to Biofiltration and Air Pollution Control
Air pollution control is a persistent challenge across multiple industries — from wastewater treatment to chemical manufacturing, food processing, and beyond. As regulations grow stricter and communities demand cleaner operations, companies are turning to biofiltration as a sustainable, cost-effective approach for treating emission streams containing odours and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
Biofiltration harnesses the natural power of microorganisms to degrade pollutants. When contaminated air is passed through a biologically active filter bed — typically composed of organic or inorganic media — microbes metabolise the contaminants, converting them into benign substances like carbon dioxide, water, and biomass, without producing hazardous effluents.
Because biofiltration relies on biological processes rather than harsh chemicals or energy-intensive systems, it is particularly resonant with the emerging ethos of eco-industrial development. In the following sections, we’ll explore how biofiltration works, its advantages, where it is commonly applied, and why modern industrial operators are increasingly adopting Tecnium-BIO systems to integrate cleaner air control into their operations.

How Biofiltration Works
Biofiltration is based on a simple yet highly effective biological principle: certain microorganisms can break down air pollutants and transform them into harmless by-products. The process typically follows three main stages:
- 1
Capture – Contaminated air is extracted from industrial processes and channelled into the biofiltration unit. This step requires an efficient collection system to ensure pollutants are properly directed toward treatment.
- 2
Conditioning – Before the air reaches the biofilter, it is adjusted to create favourable conditions for microbial activity. This may involve controlling humidity, temperature, and removing dust or harmful substances that could inhibit the bacteria.
- 3
Biological Cleaning – The preconditioned gas passes through a packed bed of organic or inorganic media where microorganisms are present. These microbes metabolise volatile organic compounds (VOCs), hydrogen sulphide (H₂S), mercaptans, and other odorous substances, turning them into water, carbon dioxide, and additional biomass.
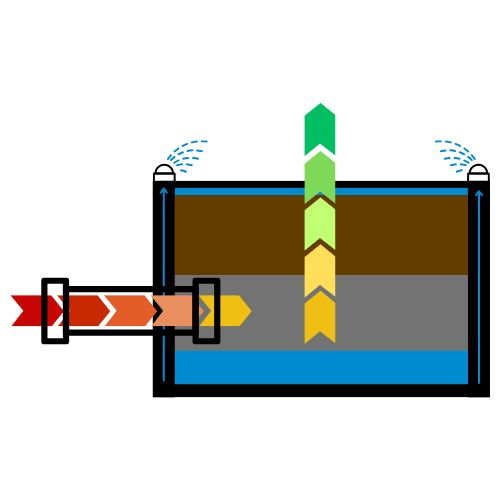
Unlike chemical scrubbers or thermal oxidation systems, biofiltration is a low-energy, low-chemical solution. Its efficiency relies on maintaining the right environment for microbial communities, which adapt over time to handle variations in pollutant load and gas composition.
This makes biofiltration especially effective in treating odours and air emissions from wastewater treatment plants, food processing facilities, and other sectors dealing with biodegradable gases.
By combining efficiency, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness, biofiltration has positioned itself as a preferred option for companies seeking to reduce their environmental footprint while maintaining operational reliability.
Industrial Applications of Biofiltration
Biofiltration is not limited to a single industry. Its versatility makes it applicable in a wide range of sectors where air pollution and odour emissions are a concern. By leveraging biological processes instead of chemical or thermal solutions, it provides a sustainable option for different industrial contexts:
Wastewater Treatment Plants (WWTPs)
One of the most common applications of biofiltration is in wastewater treatment facilities, where gases such as hydrogen sulphide (H₂S) and mercaptans generate strong odours. Biofilters are widely used to reduce these emissions and ensure compliance with environmental regulations, while also improving the quality of life for nearby communities.

Food and Paper Industries
In food processing plants and paper mills, emissions of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and odorous gases can be significant. Biofiltration offers a natural and cost-effective method to control these emissions, ensuring safer and cleaner operations.

Chemical and Pharmaceutical Sectors
Facilities that handle solvents, chemical by-products, or pharmaceutical manufacturing often release biodegradable compounds into the atmosphere. Biofilters provide a solution to treat these emissions without creating additional waste streams, aligning with stricter industry standards.

Other Industrial Fields
Biofiltration is also applied in the fertiliser industry, biogas plants, and waste management sites. In each case, it helps mitigate odour nuisance and reduce harmful emissions, contributing to both environmental protection and regulatory compliance.

This broad adaptability highlights why biofiltration has become one of the most effective and environmentally responsible solutions for air pollution control across multiple sectors.
Biofiltration vs. Conventional Air Pollution Control Methods
When it comes to air pollution control, industries can choose from several technologies. Below is a direct comparison between biofiltration and other conventional methods:
Biofiltration
Chemical Scrubbers
Activated Carbon Adsorption
Thermal Oxidation
Biofiltration is the most sustainable option when dealing with odours and biodegradable VOCs, offering low costs and minimal environmental impact. However, when pollutants are non-biodegradable, toxic, or highly variable, conventional methods such as scrubbers, carbon filters, or thermal oxidisers may be required — either independently or as part of hybrid systems that combine the strengths of multiple technologies.
Biofiltration as a Strategic Path to Cleaner Air
Biofiltration has established itself as a proven and sustainable technology for air pollution control. By combining natural biological processes with engineering design, it offers industries a cost-effective way to eliminate odours and volatile organic compounds while reducing environmental impact.
In a regulatory landscape increasingly shaped by sustainability and circular economy principles, biofiltration provides a forward-looking solution that aligns with both compliance requirements and corporate environmental responsibility.
Looking for reliable biofiltration systems?
Contact Tecnium today to learn how our TECNIUM-BIO solutions can help your facility achieve cleaner air, lower operational costs, and stronger environmental performance.

